by Eric Rueth
On February 24, The American Alpine Club will celebrate the first American ascent of the world’s second-highest peak, K2, at our Annual Benefit Dinner in Boston. It’s been 40 years since Jim Whittaker led an American expedition to the Savage Mountain but the history of American expeditions to the mountain goes back much farther and is one mired in adventure, tragedy and heroism.
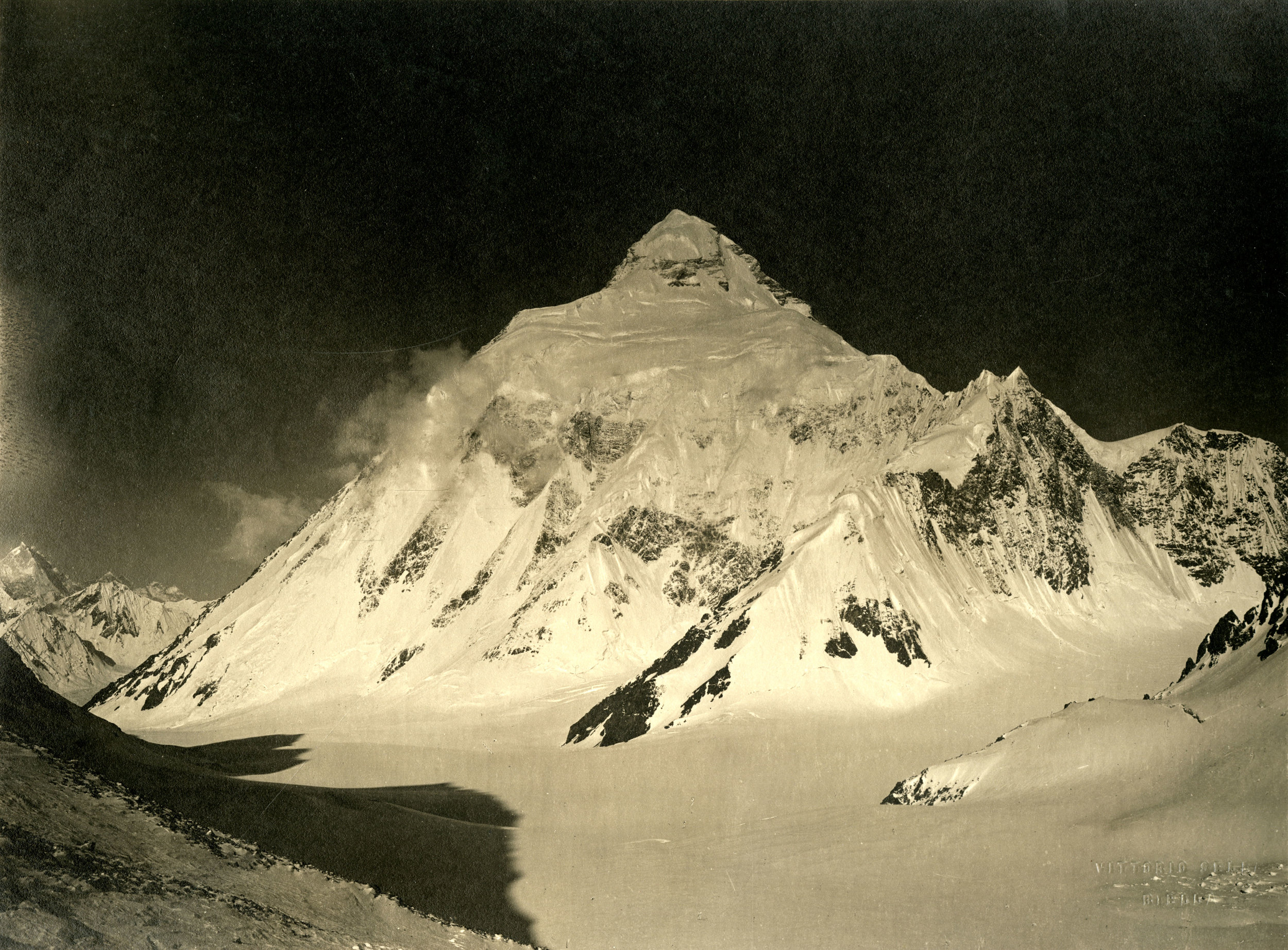
Photograph of K2 from the Baltoro Glacier, taken by Vittorio Sella in 1909. Vittorio Sella Collection
The first American expedition to K2 took place in 1938. This was not only the first American expedition to the mountain but the 3rd ever attempt on the mountain and the first since the Duke of Abruzzi attempted K2 in 1909. The American Alpine Club had acquired permits to K2 for 1938 and 1939. With permits for back-to-back years, the main focus for the 1938 expedition was to reconnoiter the mountain and three ridges to determine the best route to the top. Of course if the opportunity presented itself they should reach the summit.
After evaluating photographs and surveys of the area from previous expeditions, it was determined that there were five potential routes. This meant there were five routes that had to be explored and hopefully at least one with a viable route to the summit.
The party, given the task that was laid before them, was relatively small. It included Charles Houston, Robert Bates, Paul Petzoldt, Richard Burdsall, Bill House, Captain Norman Streatfeild (British Liaison Officer), 6 Sherpa porters and 3 camp men.
On May 13, 1938 the party departed Srinagar to begin their 362-mile approach. After a month the confluence of the Savoia and the Godwin-Austen glaciers was reached on June 12. The confluence of the glaciers provided a centralized basecamp that allowed the expedition to have relatively easy access to both glaciers for reconnaissance.
Once base camp was established at 16,600 ft., the first task was to reconnoiter the Northwest Ridge. The ridge looked promising in photographs taken by the Duke of Abruzzi’s expedition, and two of his guides had reached the Savoia Pass on the ridge. After navigating over the crevasse covered glacier, Houston and House reached the bergschrund only to find disappointment in the form of hard green ice. It was fewer than 800 feet to better terrain above but they determined that chopping steps into the ice would be too consuming of time and energy and would be a dangerous link in the chain of camps up the mountain if the Northwest ridge offered a viable route. Fortunately, Petzoldt and Burdsall spied a rock route that they believed could unlock the ridge. When House and Petzoldt made an attempt to see if the rock route would go, they were met with unfavorable weather and had to abandon the thought for the moment.
On June 19th the entire party convened at basecamp to discuss what had been discovered thus far and how to proceed. Bates and Burdsall had made a trip down the Godwin-Austen Glacier and through brief clear weather windows were able to completely rule out the south face due to avalanche danger. After a good look at the Abruzzi Ridge, they reported that it didn’t look promising.
The northwest ridge wasn’t out of the question, but the obstacle of ice would be a time consuming one. So, the focus shifted to the east side of the mountain. The expedition would get a close look at the Abruzzi Ridge and the northwest ridge and return to the Savoia glacier if no route seemed better than what had already been discovered on the northwest ridge.
Continuing with the trend, the first views from the east side of K2 were not positive. The northeast ridge is a long knife-edge ridge littered with gendarmes. The south side of the ridge seemed like it could go but would require long stretches of travel through icy gendarmes that could topple over onto anyone traveling beneath them. The north side was prone to avalanches from high up the mountain and neither appeared to offer sites suitable for establishing camps. The Abruzzi Ridge at least looked possible, though difficult.
After the first views of these two ridges it was decided that Houston and House would climb the Abruzzi Ridge to determine the difficulty of climbing. On the first day of exploration of the ridge Houston discovered some small pieces of wood, these were remnants of the Duke of Abruzzi’s highest camp in 1909 and provided a psychological boost to the climbers. As they carried on up the ridge, the climbing grew more difficult and no suitable campsites were found. With the Karakoram’s penchant for sudden poor weather, the lack of adequate campsites was more concerning than the difficulty of climbing.
Photograph of K2 from Windy Gap, taken by Vittorio Sella in 1909. Vittorio Sella Collection
Uncertainty began to set in. Three routes remained as options: the northwest ridge, the northeast ridge and the Abruzzi Ridge. The big problem was that none of the routes seemed particularly better than the others. Each ridge had its own question looming over it. Could the northwest ridge be reached without devoting a lot of time and energy to carve out steps? Was there a potential route hidden on the northeast ridge that would not place the climbers in extreme danger? Were there any suitable locations to place campsites on the Abruzzi Ridge?
The party attempted to answer two of these questions. Bates and House returned to the Savoia Glacier. A few days of roaring avalanches off of the west face of K2, tumbling seracs, traversing ice slopes and heavy snow saw the pair reach a high point of 20,000 ft. before the rock became too steep. They came to the conclusion that reaching the northwest ridge under the current conditions was not possible.
Houston and Streatfeild had an easier time on the northeast ridge; easier in that they realized after several hours of step cutting that the route would not be adequate for carrying loads and the ridge offered little protection for any campsites that could be established.
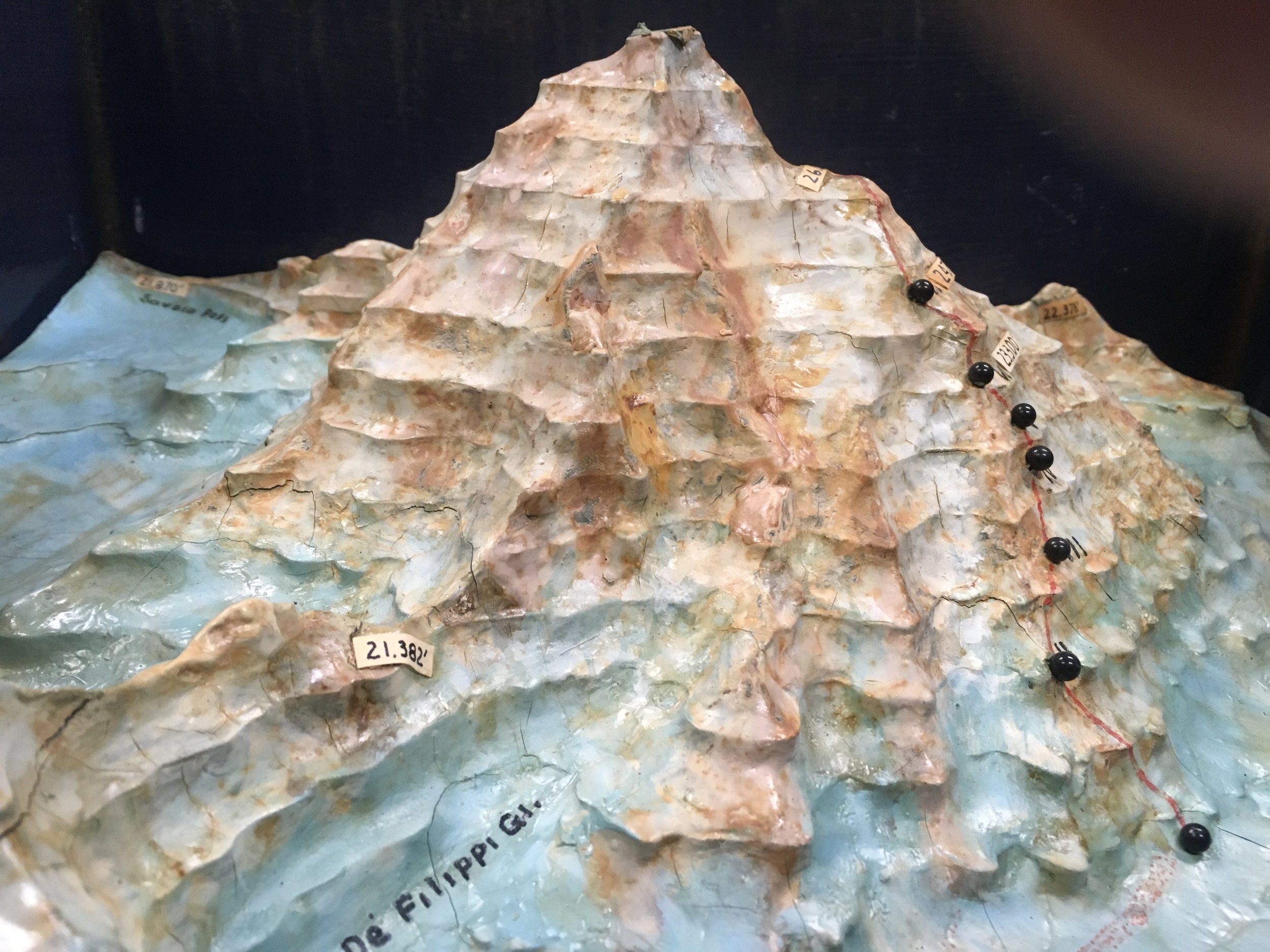
So the Abruzzi Ridge was all that remained. As the last viable option all efforts and resources would now focus on the Abruzzi Ridge. Camp I was established at its base at 17,700 ft. While the rest of the expedition ferried loads to stockpile Camp I, Petzoldt and House continued scouring the ridge for campsites. After a day of searching and ascending a steep snowfield, hopes were waning and the pair was about to descend back to Camp I. Petzoldt decided to ascend one more pitch to peek around the corner of a crest. When Petzoldt reached the end of the rope, he let out an excited yell. Camp II was found. The campsite at 19,300’ was the first good news of the expedition since arriving the base of the mountain and lifted everyone’s spirits.
Rock taken from the Abruzzi Ridge. Karakoram translates to, "black gravel." Robert H. Bates Collection
Once Camp II was established and stocked with 10 days worth of supplies Petzoldt and House again led the way in search of the next camp. The ground grew steeper and steeper with any ledges discovered sloping downward. Once again the prospect of finding a campsite seemed slim and hopes began to waver. Around noon, as the going became more and more difficult, the pair noticed two buttresses a few hundred feet above them that may yield suitable terrain. With haste House began the first of two ice traverses that lay between them and the buttress. In an effort to save time House cut as few steps as possible. This time-saving maneuver led to House losing purchase and sliding towards the Godwin-Austen Glacier. Petzoldt was prepared for this possibility and held fast to the rope around House’s waist. After banging into the buttress that Petzoldt belayed from, House attacked the ice slope with new vigor. House completed the traverse placing pitons and running rope along the way. The reward for the day’s climbing was a tiny, uneven platform that sloped off the mountain on three sides.
Before Camp III (20,700 ft.) could be established Petzoldt and House needed to safeguard the route with 900 ft. of rope. The treacherous terrain was difficult for two unloaded men; it would be near impossible and reckless to attempt with a full load of supplies. The task of safeguarding the route took the entirety of the next day and still not satisfied with its security, was reinforced more as light loads were carried towards Camp III the day after that. Before the light loads could be brought all the way to Camp III, a storm began to build. The loads were left below a buttress and the pair descended all the way to Camp I when it appeared that the storm was gaining strength and was potentially going to be a long one.
The storm was not prolonged and the next day was relatively clear. With extreme caution, loads were carried to Camp III and more ropes placed to further secure the treacherous sections of the route. After 4 days of ferrying loads while snow fell and winds howled around them it was time to go higher than Camp III and search for Camp IV.
Petzoldt and Houston led the way in search of Camp IV. The climbing above Camp III grew more technical, the rock grew more rotten and was eventually blocked by a large gendarme. Petzoldt conquered the obstruction via an overhanging crack that led to a ledge with solid holds. A few hundred feet above the recently defeated gendarme another obstruction was reached, this time it was an impassable wall of reddish-brown rock. The duo descended back to the top of the gendarme and decided that it would be the location for Camp IV (21,500 ft.).
Once Camp IV was established it was time to push up the mountain. The new leaders were Houston and House. A location for Camp V was discovered at 22,000 ft., placing it only 500’ higher than Camp IV.
Above Camp IV the rock was near vertical and in worse condition than expected. This section was only climbed after House was able to work his way up an 80-foot chimney. The chimney now bears his name. Camp V was then located across a snowfield and under a rock pinnacle. This 500’ took four hours to achieve and would be an entire days work when moving supplies. House’s Chimney was impossible to climb with a load so a makeshift aerial tramway was constructed to haul the loads up.
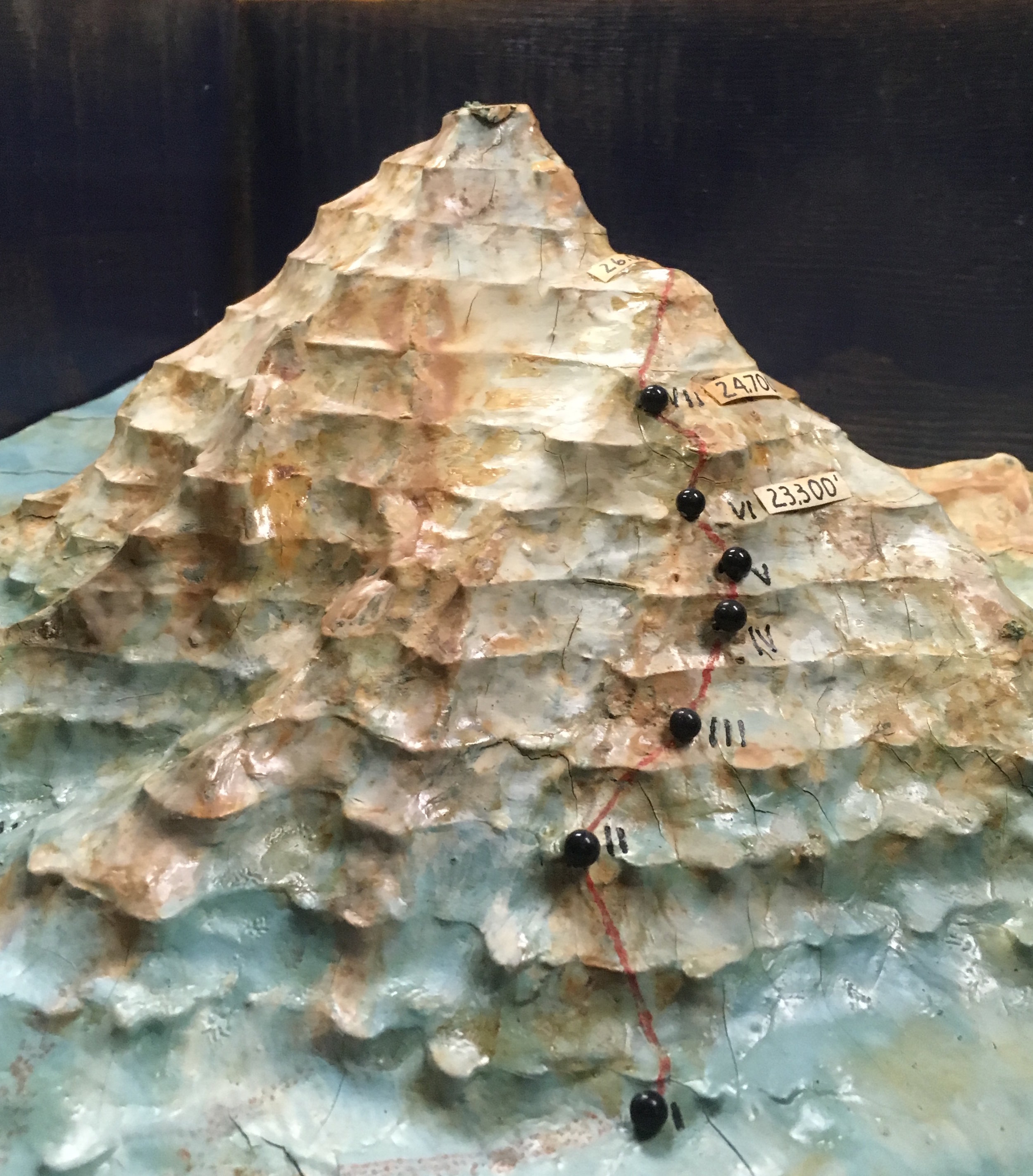
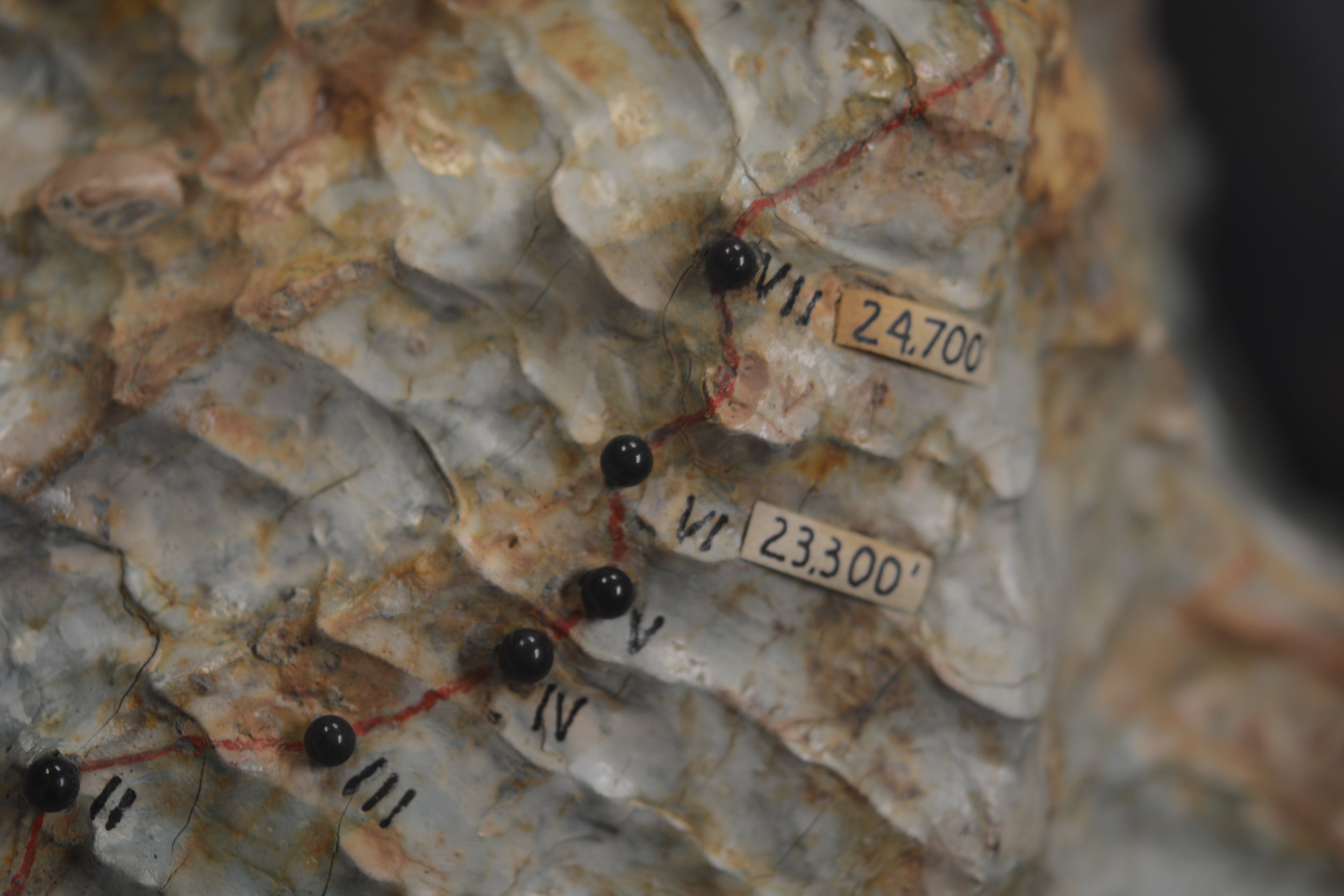
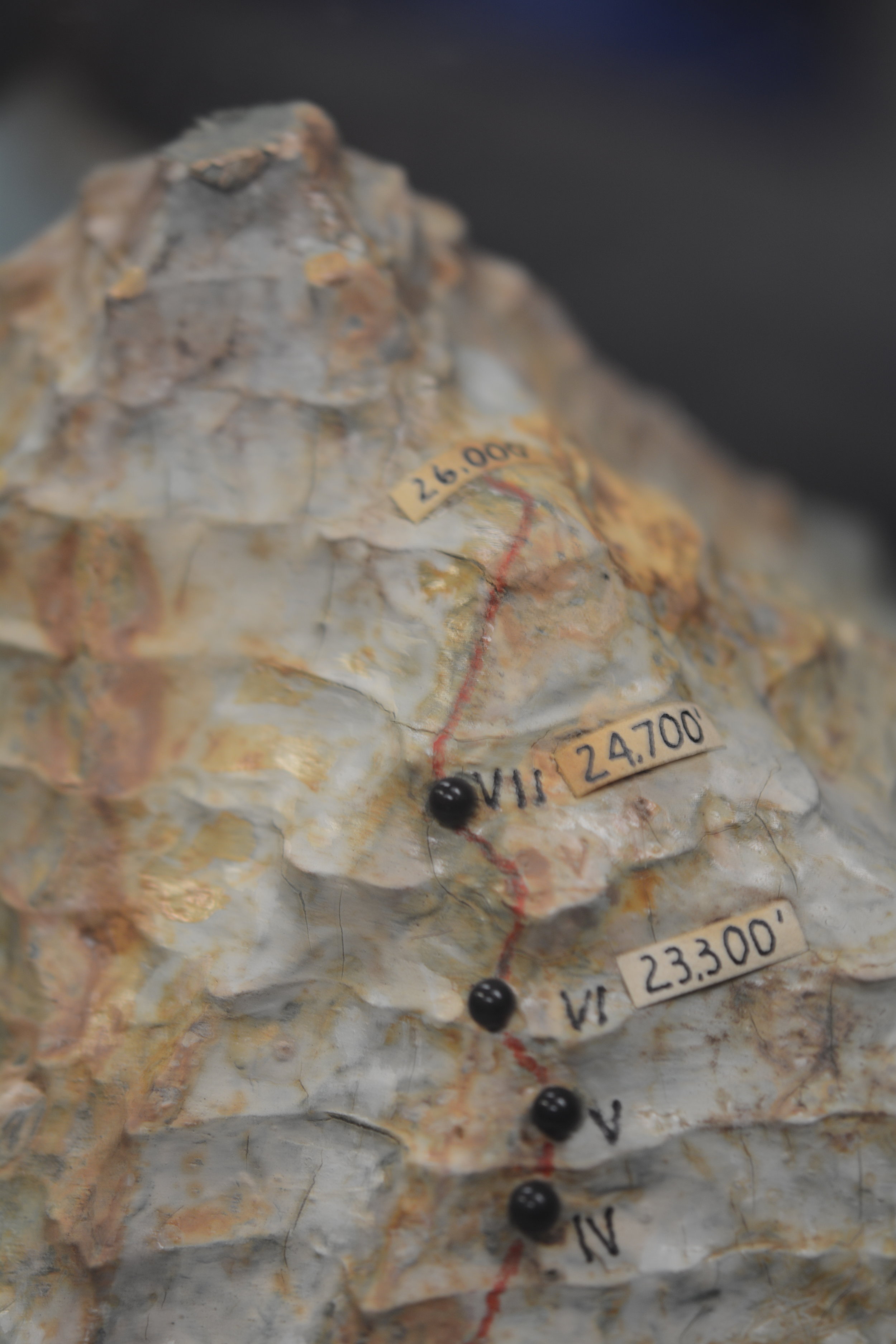
After a few days of poor weather and load ferrying, a site for Camp VI was discovered at 23,300’. The climb up to Camp VI took serious skill in route finding and saw Petzoldt and Houston turned back at multiple points. Eventually they discovered a steep snow gully that tested their nerves. The snow was deep and anything that fell down the gully disappeared into nothingness. The snow gully led to more rotten rock, which led to a buttress whose base would be the location for Camp VI.
Above Camp VI lay the black pyramid, a near 1,000-foot buttress of dark rock that loomed over the expedition while they were scouting the ridge a month earlier. If they could make their way up the black pyramid, K2’s 2,200-foot summit cone would be within reach.
Petzoldt and Houston worked their way up the route; Petzoldt, with fine intuition about where the path lay ahead, led over steep technical rock and eventually up another snow gully that led to the top of the pyramid. With the snow shoulder above the black pyramid reached, the Abruzzi Ridge was conquered. A handshake was shared and a “restful cigarette” enjoyed.
Thank you note written by Houston and Petzoldt on a piece of toilet paper. It reads:
"Hi
Thanks a million for the campsite and tent. They were certainly welcome when we came down at 4:15. Very cold.
We went 700 ft. higher over climbing of varying difficulty and spotted c/c weather. Route ahead not too bad. Hope to make top of pyramid today.
We hoped you could make two platforms more on this ledge and one near the big notch [?] feet below here.
Good luck + thanks again
C +P"
Robert H. Bates Collection
The route was pushed higher and a good campsite was found for Camp VII at 24,700 ft. Even after ropes were fixed on the difficult terrain between Camp VI and VII, the route would remain difficult and would be unwise to attempt in bad weather. With supplies dwindling it was time to make a decision.
The expedition conceded to K2 and the mountain remained unclimbed. With supplies dwindling and difficult terrain between camps a prolonged storm would potentially be catastrophic to the group, added onto that the porters were due to arrive in seven days.
Before retreating down the mountain, one final push would be made. Houston and Petzoldt would make a dash as high up the mountain as they could reach. A Spartan Camp VII was established with just enough supplies for Houston and Petzoldt to climb for a day. Any sign of bad weather would force the pair to make a hasty retreat to Camp VI.
The weather the next day was clear so the pair went up. Though K2 had provided many difficult and technical days of climbing, the final day was one of plodding through snow. By noon a recognizable shoulder was reached at 25,600 ft. The Duke of Abruzzi had triangulated the altitude 29 years earlier and the climbers knew that they had reached the summit cone. The pair climbed up a few hundred more feet to gain a good view of the route that led to the summit. Both agreed that it did not appear any more difficult than the route below and that the summit could be reached from the Abruzzi Ridge. They then turned and started back down the mountain.
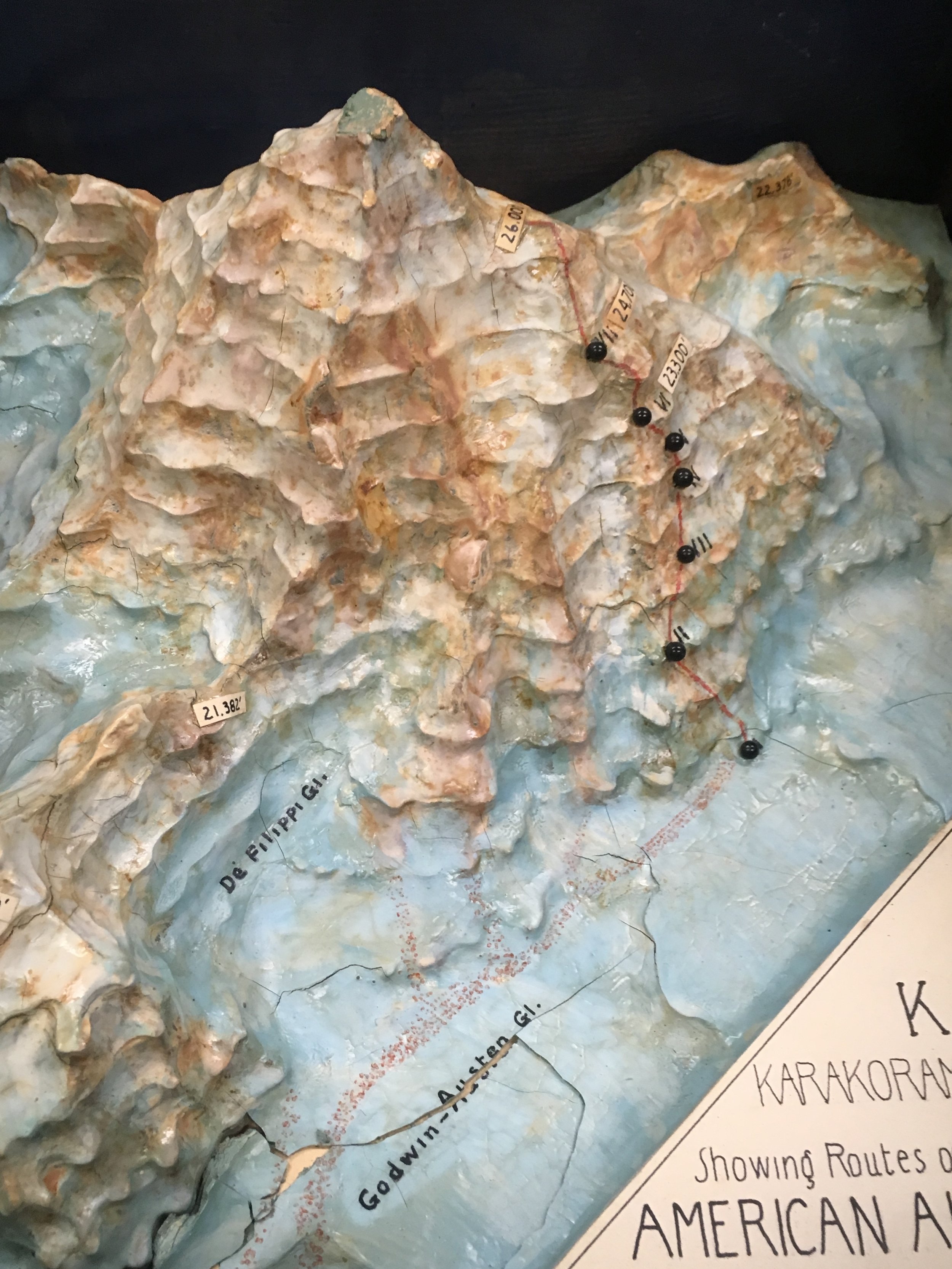
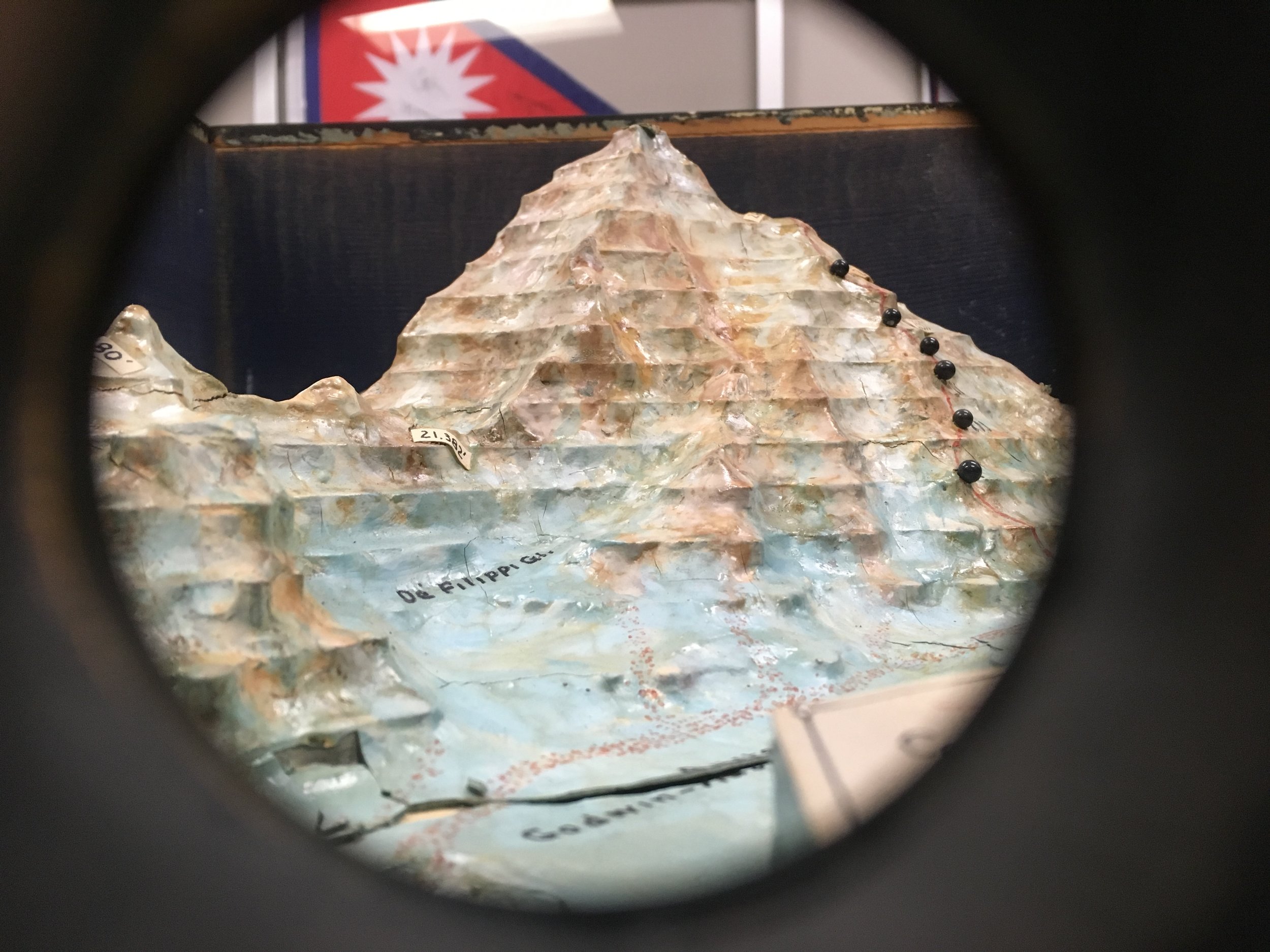
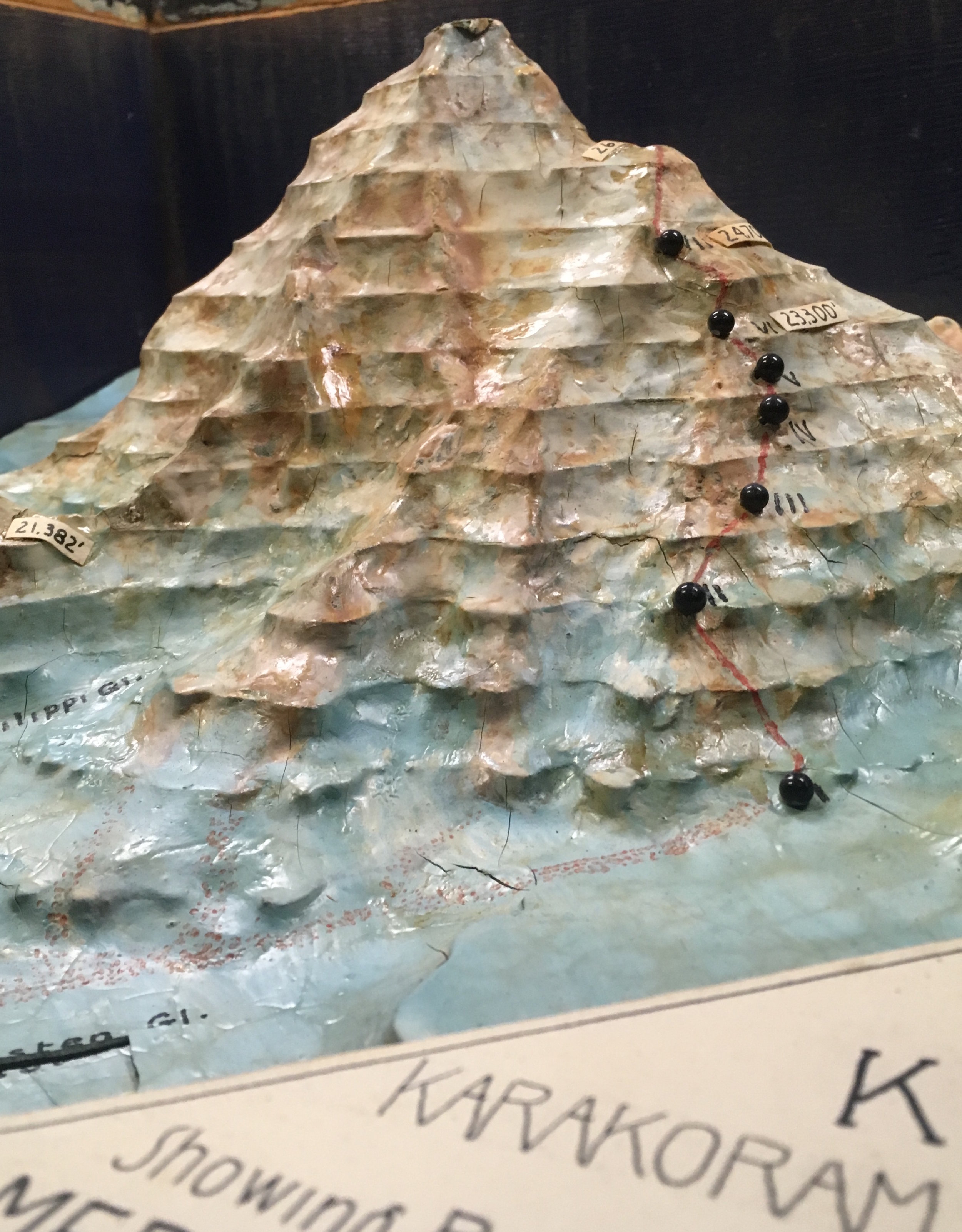
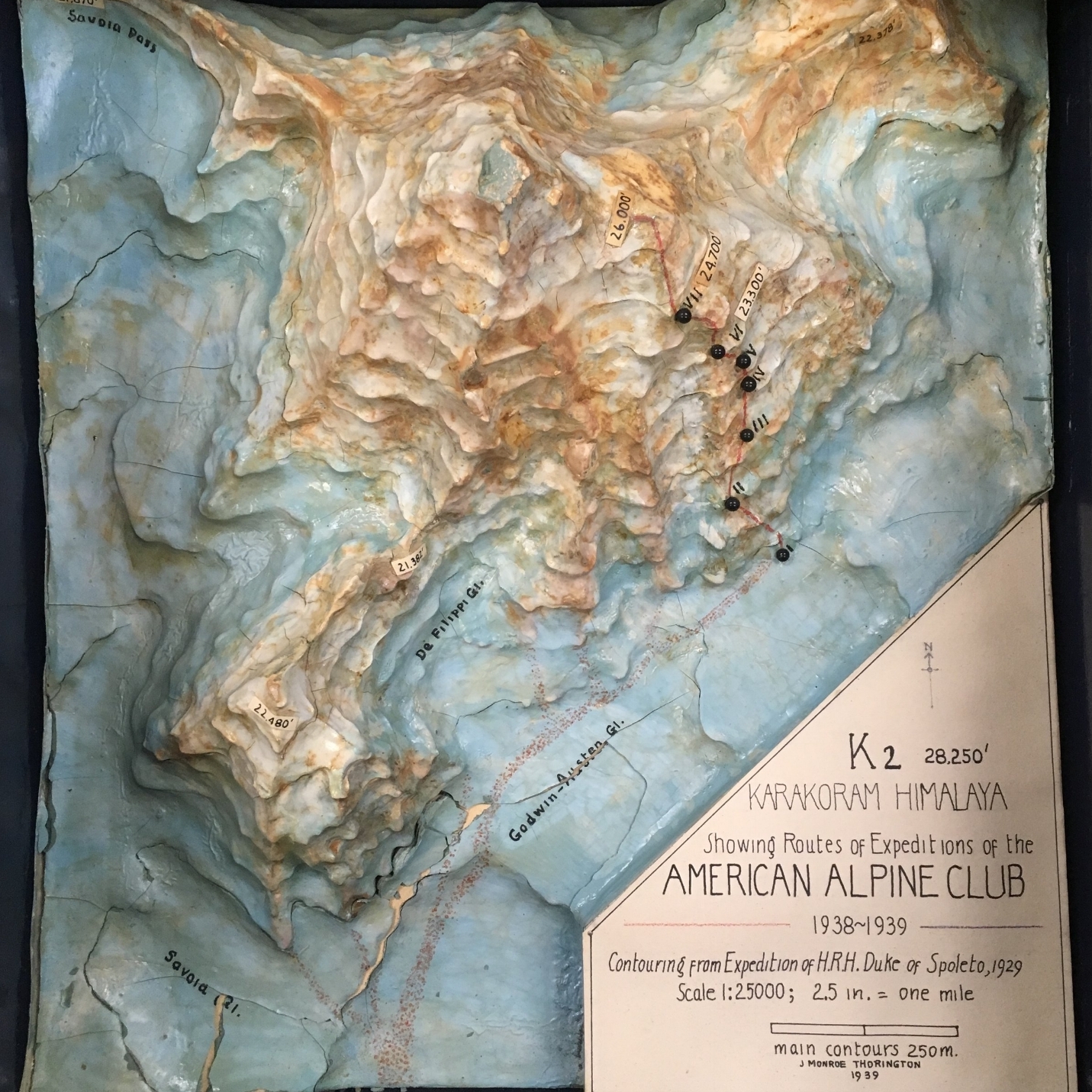







Though their high point of 26,000 ft. was 2,250 ft. below the summit, the First American Karakoram Expedition was a success. The entire south side of the mountain was reconnoitered and a promising route to the summit was discovered. More importantly there were no major injuries and everyone involved survived the attempt high up the Savage Mountain. It was now up to the Second American Karakoram Expedition to climb the mountain.
Read about the Second American Karakoram Expedition here.
Read about the Third American Karakoram Expedition here.
By Eric Rueth




